|
|
|
-
lim (1 + 1/x)x = e
x->inf
-
lim (1 + x)1/x = e
x->0
-
L(1 + x)
lim -------- = 1
x->0 x
L(1 + x) 1 (*) por límite tipo 2
lim ------- = lim --L(1 + x) = lim L(1 + x)1/x = lim Le = 1
x->0 x x->0 x x->0 x->0
(*) Pues bLa = Lab
-
ex - 1
lim ------- = 1
x->0 x
Cambio de variable: ex - 1 = y
lim y = 0
x->0
ex = 1 + y => Lex = L(1 + y)
xLe = L(1 + y) (pues Lab = bLa)
x = L(1 + y) (pues Le = 1)
y y 1
lim -- = lim -------- = lim ------- = 1
y->0 x y->0 L(1 + y) y->0 L(1 + y)|
------- |-> 1 por límite tipo 3
y |
-
ax - 1
lim ------ = La (a perteneciente a R+)
x->0 x
Cambio de variable: ax - 1 = y (limx->0 y = 0)
ax = 1 + y
Lax = L(1 + y)
xLa = L(1 + y)
L(1 + y)
x = --------
La
y y La
lim -- = lim ------- = lim ------- = La
x->0 x y->0 L(1 + y) y->0 L(1 + y) |
------- ------- | -> 1 por límite tipo 3
La y |
-
sen x
lim ----- = 1
x->0 x
Consideremos el círculo trigonométrico (círculo de radio 1).
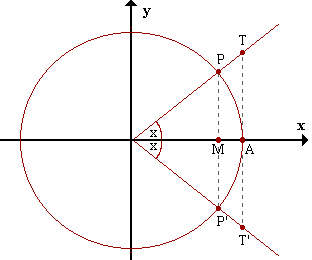
Si x > 0
x = ÂP (Recordar que el ángulo x se mide por la longitud
sen x = MP del arco AP, independientemente de la unidad
tg x = AT utilizada, que puede ser por ej. grados o radianes).
Si x < 0
x = ÂP'
sen x = MP'
tg x = AT'
MP < AP < AT, o sea, sen x < x < tg x, para x > 0 (1)
MP' > AP' > AT', o sea, sen x > x > tg x, para x < 0 (2)
Dividimos (1) y (2) entre sen x (que es negativo cuando x < 0)
y obtenemos:
x tg x
1 < ----- < -----
sen x sen x
sen x sen x
1 > ----- > ----- = cos x -> 1
x tg x x->0
sen x
Por teo. de la función comprendida lim ----- = 1
x->0 x
tg x
lim ---- = 1
x->0 x
tg x sen x sen x
lim ---- = lim -------- = 1 pues lim ----- = 1 por límite
x->0 x x->0 (cos x)x x->0 x tipo 6
y lim cos x = 1
x->0
1 - cos x 1
lim ---------- = --
x->0 x2 2
cos2x + sen2x = 1 => sen2x = 1 - cos2x (1)
1 - cos x (1 - cos x)(1 + cos x)
lim --------- = lim ---------------------- =
x->0 x2 x->0 x2(1 + cos x)
1 - cos2x por (1) sen2x 1
lim ------------- = lim ------------- = --
x->0 x2(1 + cos x) x->0 x2(1 + cos x) 2
sen2x
pues lim ----- = 1 por límite tipo 6 y lim 1 + cos x = 2
x->0 x2 x->0
(1 + x)m - 1
lim ------------- = 1
x->0 mx
(1 + x)m - 1 (1 + x)(1/x)xm - 1 por límite tipo 2
lim ------------ = lim ----------------- =
x->0 mx x->0 mx
emx - 1
lim ------- = 1 por límite tipo 4
x->0 mx
n ______
\|1 + x - 1 1
lim ------------- = --
x->0 x n
n _____
\|1 + x - 1 (1 + x)1/n - 1 (1 + x)(1/x)x(1/n) - 1
lim ---------- = lim ------------- = lim --------------------
x->0 x x->0 x x->0 x
por límite tipo 2
ex/n - 1 ex/n - 1 1 por límite tipo 4
= lim -------- = lim -------- = --
x->0 x x->0 (x/n).n n
<< anterior siguiente >>
|
|
Página principal
Tabla de Contenidos
Noticias matemáticas
|